Asset Type
This is a Claude Project created to be re-usable, as if it is software running on top of the LLM. Claude Projects are organizations of files and instructions that are efficiently added to Claude's context window. The instructions below will focus on implementing the asset in Claude as a Project, but the assets in this Claude Project should be usable outside of a Project, including with other LLMs.
This has subsequently been packaged as a Claude Skill, which may be easier for you to use as it requires fewer steps. Note that the Claude Skill version will use more tokens, due to the interactive nature of the information gathering process. See here for the Claude Skills formulation.
Purpose
The Learning Plan Generator takes personalization input and a learning objective and generates a sequence of reading, watching, and doing to achieve the learning objective.
Overview
This Claude Project generates a personalized learning plan for an arbitrary topic:
- selectively extracts relevant and mostly free learning content from across the web
- chooses content based on your learning style (doing, reading, watching, etc.)
- sequences content rationally for dependencies and prerequisite knowledge
- excludes content covering what you already know
- excludes content that doesn't support your learning objective
This solution takes the following basic steps:
- Work with Claude to set a learning objective
- Work with Claude to elaborate the learning objective into learning items
- Ask Claude to generate a learning plan to meet the learning objective, using the learning items and example learning plan as guides
The Learning Bootstrapping Problem
Let's consider the alternative approach to learning a topic you're interested in. If you were to put together your own learning plan manually, there is a chicken-and-egg problem, where you do not know enough about the overall topic and its subtopics to understand prerequisites and dependencies between subtopics. This bootstrapping problem leads most learners to seek out a single primary source from an expert, such as a comprehensive book or tutorial. When designing the asset, the expert thought through the progression of topics. Thus, a single comprehensive source is often the backbone of a learning plan (a college course uses a textbook, learning programming in a new language often uses a main tutorial from the language's governance organization, etc.), and then the learner supplement on top of that backbone.
How Claude Solves This
The learning plan Claude develops uses no single comprehensive source as its foundation. The learning plan consists of many resources from different places all over the web. Claude finds, organizes, and sequences the best learning content it's aware of, personalized to you based on your existing knowledge and learning style, and sequenced according to its understanding of prerequisites and dependencies.
Claude selectively extracts relevant learning content from comprehensive sources. Claude may include an online course, but Claude's learning plan might say to do only units 3, 6, and 8 (for example) because these support the learning objective, while the other units either don't support the learning objective or are better covered by other sources.
Claude synthesizes expertise from multiple sources by constructing the dependency graph from its training data and web searches, solving the chicken-and-egg problem that forces most learners to rely on a single author's sequencing.
How to Use This
1. Create a new Claude Project
Create a new Claude Project. Click "Projects" and then "New Project." You can name it whatever you want or just "Learning Plan Generator". Click "Create Project" to complete the creation process.
2. Set instructions
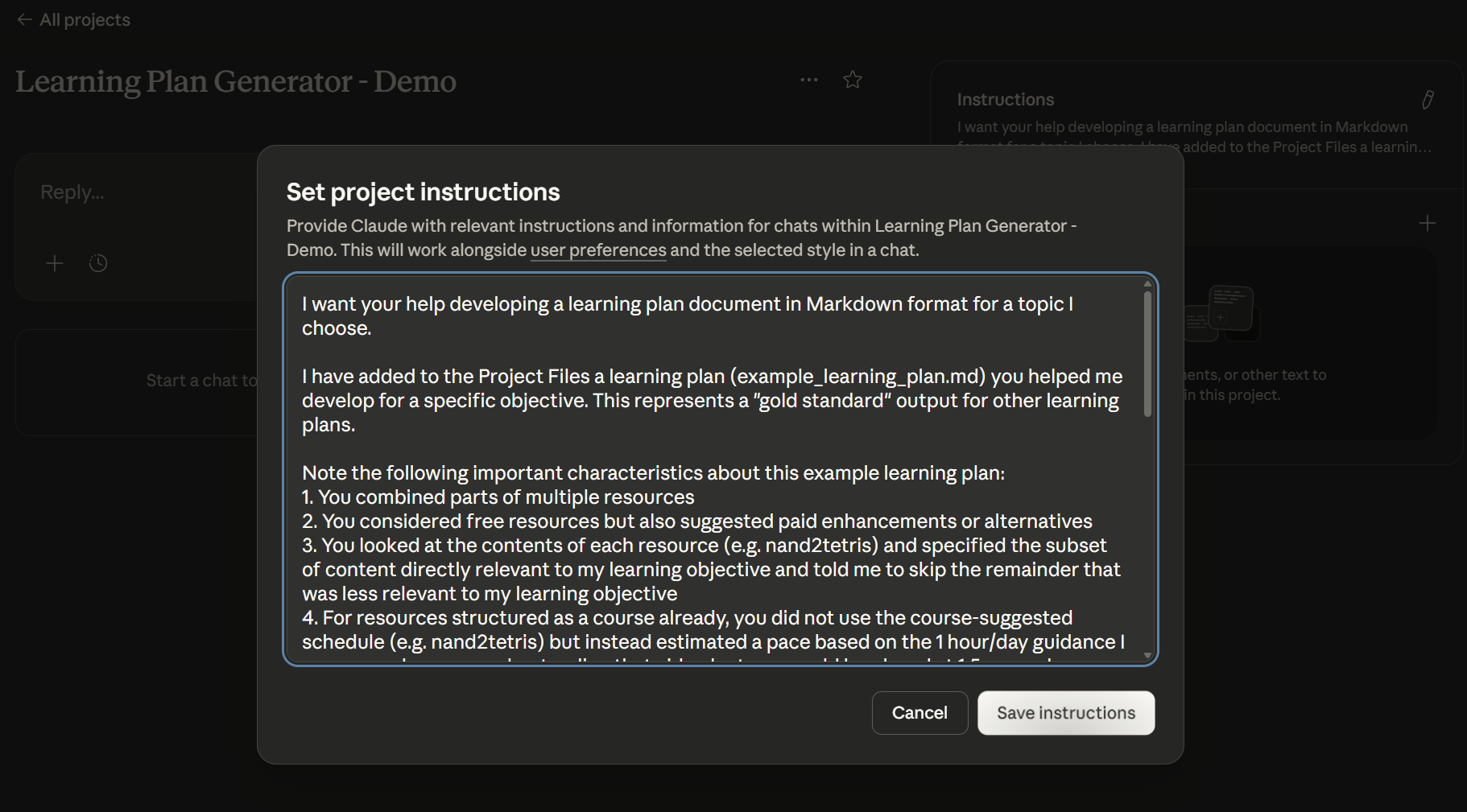
Open 0_INSTRUCTIONS.txt and copy the contents into the Project Instructions by clicking the '+' in the "Instructions" box and pasting the instructions into the "Set project instructions" modal that displays. Click 'Save instructions'.
3. Set Up Learner Profile
Modify the 1_Learner_Profile.md file to match your learning preferences. It can be hard to know what type of content works well for you and what doesn't. Just do your best. You can learn over time what your preferences are and update this file for future learning plans you generate.
## User Profile (Stable Preferences)
These preferences apply to all learning plans for this user:
### Learning Style - Strong Preferences
1. **"Designed for ~1 hour per day"** - Prefer smaller daily learning routine rather than long learning blocks on weekends
2. **"Prescriptive, canonical paths"** - One well-documented learning path per learning concept. I find choice and options within learning content to be distract from my learning objective.
3. **"High signal-to-noise ratio, theory-first"** - I learn well from reading documentation and extracting concepts. I don't need hands-on work for
...
This section also includes a negative example to show Claude what not to suggest. If you have an example of an article or course or video that is not a fit for your learning style, replace this section with that so Claude knows what to avoid. If you don't have a negative example, just delete this section.
---
### Negative Example (What NOT to recommend)
**Mike Silva's "Introduction to Microcontrollers" series** exemplifies several anti-patterns for my learning style:
- **Low signal-to-noise ratio**: Spent 6-10 hours to extract ~1 hour of useful concepts. Too much content written defensively for expert critics rather than to teach beginners efficiently.
...
4. Work with Claude to Refine the Learning Objective
Customize the prompt below to properly explain your learning objective for this learning plan. This is your first draft, and you will iterate on this with Claude.
Help me refine this learning objective narrative for why I want to learn more about AI. The narrative's purpose is simply explain to you (Claude) my learning objective so that you can help me with related tasks. We do not need to refine the language in ways that would only be relevant to a human audience (e.g. publication).
My objective for learning this topic is summarized below.
I work as an executive in an education data and technology consulting company, where I've been for almost 15 years. AI adoption in education is still nascent, and practical applications remain limited. Understanding AI's technical foundations and capabilities should help me identify realistic opportunities to address education industry problems.
People in my network often ask me to reality-check their ideas about new technologies. To provide useful feedback on AI-related proposals, I need a stronger grasp of implementation principles, current limitations, and what's actually feasible versus speculative.
I also expect AI competency to become foundational across careers, similar to how computer literacy evolved from a specialized skill to a universal requirement. Building this competency now should prove valuable even in ways I cannot currently anticipate.
Within the Project, put your cursor in the chat box and paste the contents of your modified prompt into the chat box. Select 'Sonnet' for the model, if not already selected, and submit the chat by clicking the up arrow button.
Feel free to converse with Claude to refine the learning objective further, until you are happy with it. Claude is about to do a lot of work for you, so spending a little extra time on this step can avoid a lot of wasted tokens from Claude missing the mark on what you need.
Once you're happy with the learning objective, copy its final form into 2_LEARNING_OBJECTIVE.md.
5. Modify Prior Knowledge
You may already have some knowledge on this topic. The Learning Plan Generator is designed to exclude content covering areas you already understand. Open 3_Prior_Knowledge.md and describe what you already know. Claude is familiar with popular educational resources in its training data, so if you've watched a video or read documentation, simply mention the resource by name rather than listing every topic it covers; Claude will account for that content accordingly.
### Knowledge I already have on this topic
* Topics covered in Karpathy's "Deep Dive into LLMs" video
* Personal and professional use of Claude, ChatGPT, and Gemini, as well as secondary tools like editGPT
* Regular requests to Claude for meta analysis of why and how Claude answered the way it did
6. Upload Project Files
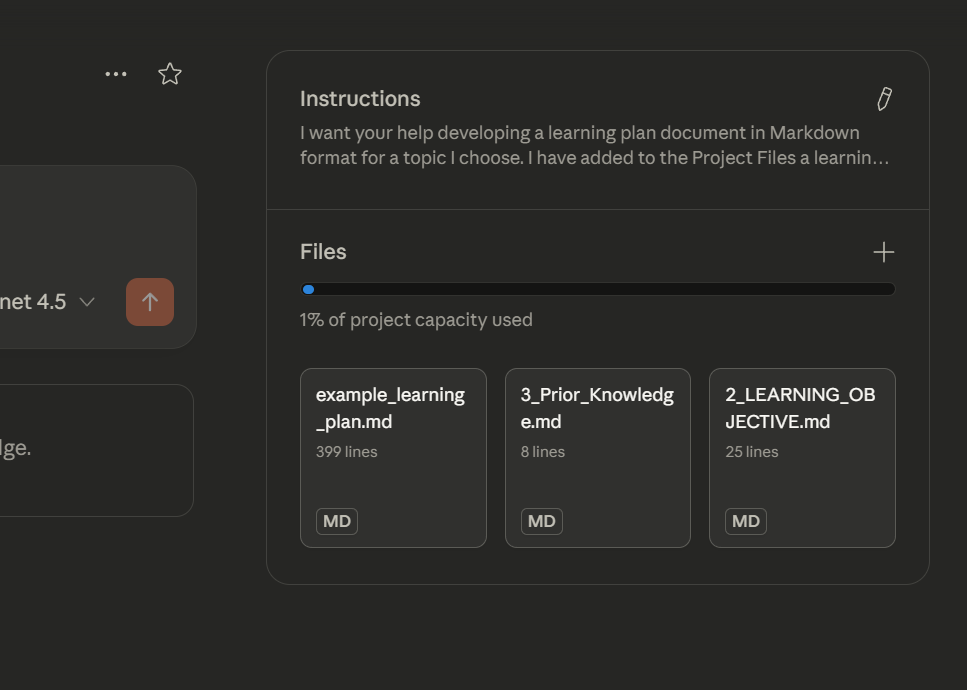
Upload 2_LEARNING_OBJECTIVE.md, 3_Prior_Knowledge.md and example_learning_plan.md to the Project Files by clicking the '+' in the Files box and selecting 'Upload from your device'
7. Elaborate Learning Objective into Concept Areas
Within the Project, open a new chat with Claude and use the following prompt.
Refer to my learning objective described in `2_LEARNING_OBJECTIVE.md`. Elaborate my learning objective into concept areas. You MUST exclude concept areas I already know, as described in `3_Prior_Knolwedge.md`.
Here is an example content areas elaboration for a learning objective related to practical applications of AI:
# Concept Areas
## Document Purpose
This file contains learning concept areas and notes supporting a learning objective.
---
## Priority Tier 1: AI/LLM Practical Applications
### Concept Areas for Learning Content
**RAG Systems & Vector Databases**
- How retrieval-augmented generation works end-to-end
- Embedding models: how they work, tradeoffs (OpenAI, Cohere, open-source)
- Chunking strategies: size, overlap, semantic vs. fixed
- Vector database options: Pinecone, Chroma, pgvector, Weaviate, Qdrant
- Retrieval strategies: similarity search, hybrid search, reranking
- When RAG helps vs. when it doesn't (failure modes)
**MCP (Model Context Protocol)**
- Protocol specification and design philosophy
- Building MCP servers (Python, TypeScript)
- Tool definition patterns
- Integration with Claude desktop and other clients
- Security considerations for MCP servers
**Claude Skills**
- Skill architecture and file structure
- SKILL.md design patterns
- How skills interact with computer use capabilities
- Testing and iterating on skills
- When to use skills vs. other approaches
**Tool Usage Mechanics (Deep Dive)**
- How LLMs decide when to use tools vs. respond directly
- Tool call formatting and parsing
- Multi-tool orchestration and sequencing
- Error handling and retry logic
- How tool results are incorporated into context
- Tradeoffs: tool use vs. in-context information
**Claude Code for Web & Companion Infrastructure**
- How the computer use environment works (container, file system, permissions)
- Working directories: /home/claude, /mnt/user-data/uploads, /mnt/user-data/outputs
- What Claude can and cannot see/access
- How file operations work and their limitations
- Caching behavior and what Claude knows about it
- Session persistence and state management
- Network access and restrictions
**Token Economics & Context Management**
- Building on Karpathy's foundation: tokenization edge cases, BPE behavior
- Context window management strategies
- Prompt caching: how it works, when it helps, cost implications
- Cost optimization: batching, caching, model selection
- When to use smaller vs. larger context windows
- Conversation design for efficiency
**Critical Evaluation**
- When to use AI vs. traditional approaches
- Hallucination patterns and detection strategies
- Output validation techniques
- Benchmarking and evaluation frameworks
- Understanding model limitations
**Explicitly excluded** (per discussion):
- Prompt engineering (less important with newer models)
- "AI agent" framing (hype-laden; useful parts covered in tool usage and MCP sections)
You can converse with Claude to iterate on the concept areas as needed.
Copy the output into 4_Concept_Areas.md. Review and modify the file as you wish. You may wish to manually remove concept areas or add new ones.
Add 4_Concept_Areas.md to the Project Files as before.
8. Run
You're ready to go. Within the Project, open a new chat. Ask Claude to generate your personalized learning plan with the following prompt:
Develop a learning plan for SUBJECT as described in the Project Instructions and Project Files.
